How to Install phpMyAdmin apache2 on Ubuntu
https://www.hostingadvice.com/how-to/install-phpmyadmin-on-ubuntu/
Last updated
https://www.hostingadvice.com/how-to/install-phpmyadmin-on-ubuntu/
Last updated
The MySQL database system is the most popular, open-source, relational database. Many other projects, including WordPress, are backed by a MySQL database and rely on its extensive feature list and simple setup. For beginners, or those that are lazy, there is the phpMyAdmin tool to help us with the maintenance and interface of MySQL.
Accessed from your web browser, phpMyAdmin is a PHP-based frontend control panel that allows you to easily manage your MySQL databases and users, review SQL activity, import and export database backups, run searches, and more.
In this guide, we’ll cover the recommended method to install phpMyAdmin from the Ubuntu packages, and how to secure phpMyAdmin. We’ll also go over installing phpMyAdmin from source, although this is not recommended in a production environment.
Before installing phpMyAdmin, we need to meet some basic requirements:
A LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP) installed
PHP 5.2.0 or newer
12345
$ php -vPHP 5.5.9-1ubuntu4.6 (cli) (built: Feb 13 2015 19:17:11)Copyright (c) 1997-2014 The PHP GroupZend Engine v2.5.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2014 Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v7.0.3, Copyright (c) 1999-2014, by Zend Technologies
The PHP mysql or mysqli extensions
123
$ php -m | grep mysqlmysqlmysqli
MySQL 5.0.1 or newer
1234
$ mysql -vWelcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g.Your MySQL connection id is 39Server version: 5.5.41-0ubuntu0.14.04.1-log (Ubuntu)
The default Ubuntu repositories stay up-to-date with the latest stable releases of phpMyAdmin, and this is the recommended installation process for a production environment.
First, we need to make sure our local server is pulling the latest updates.
1
sudo apt-get update
Now we can install the latest version of phpMyAdmin.
1
sudo apt-get install -y phpmyadmin
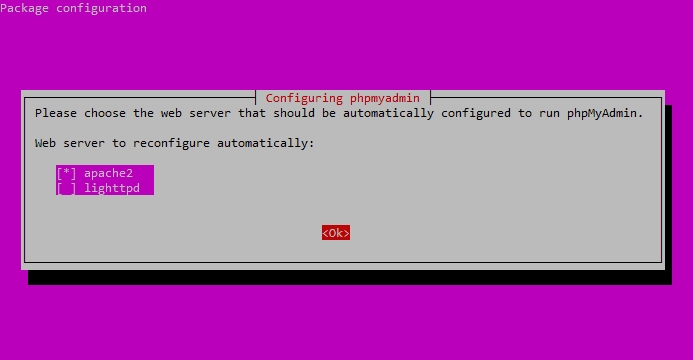
After installing phpMyAdmin, you will be presented with the package configuration screen.
Press the SPACE bar to place an “*” beside “apache2.”
Select “apache2” and hit OK.
The installation process will continue until you’re back at another package configuration screen.
Select “Yes” and hit ENTER.
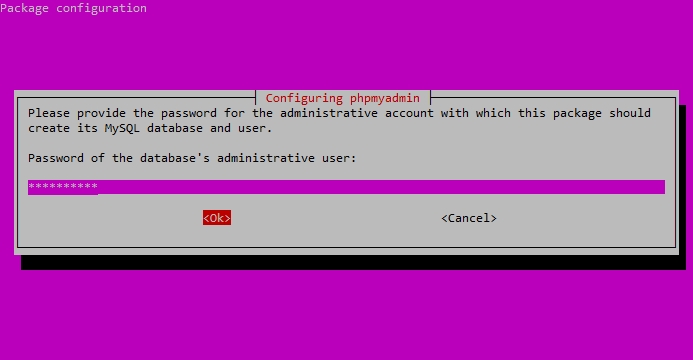
You will be prompted for your database administrator’s password.
Enter your DB administrator’s password.
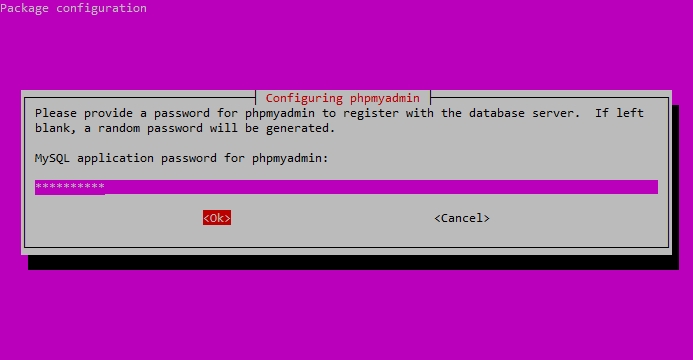
Enter the password you’d like to use to access the phpMyAdmin interface.
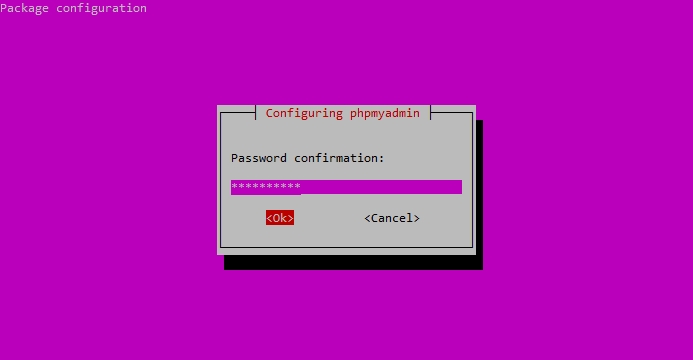
Confirm your phpMyAdmin password.
After the installation process completes, it adds the phpMyAdin configuration file here:
/etc/apache2/conf-enabled/phpmyadmin.conf
Check if the PHP mcrypt module is already in use:
1
php -m | grep mcrypt
If you don’t get any results, install the PHP mcrypt module with:
1
sudo php5enmod mcrypt
Now when we check, you should see mcrypt enabled:
12
$ php -m | grep mcryptmcrypt
Now we should restart the Apache web server for changes to take affect:
1
sudo service apache2 restart
Now you can log in to phpMyAdmin by going to your server followed by /phpmyadmin.
You can just use http://YOUR_SERVER_IP/phpmyadmin if you don’t have domains set up yet.
Log in to phpMyAdmin as the root user.
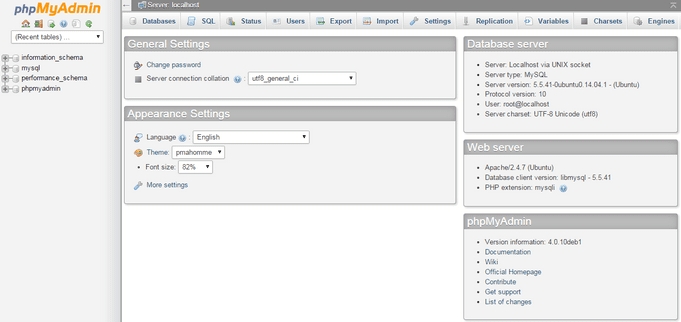
You should now see the phpMyAdmin dashboard.
Naturally, because phpMyAdmin is such a common application installed on many web servers, it is a popular target for unauthorized access attempts. We can easily secure our phpMyAdmin installation by using Apache’s built-in .htaccess authentication.
We want to edit the phpMyAdmin Apache config that was created earlier:
1
sudo vi /etc/apache2/conf-available/phpmyadmin.conf
Add AllowOverride “ALL” directive below the DirectoryIndex:
12345
Options FollowSymLinks DirectoryIndex index.php AllowOverride ALL ...
Restart Apache so our changes take affect:
1
sudo service apache2 restart
Now that we’ve enabled overrides for our phpMyAdmin application from Apache, we need to actually create an override with an .htaccess file.
1
sudo vi /usr/share/phpmyadmin/.htaccess
Add this text:
1234
AuthType BasicAuthName "phpMyAdmin Users Only"AuthUserFile /etc/phpmyadmin/.htpasswdRequire valid-user
First we need the htpasswd utility. If you don’t already have this installed, use the following:
1
sudo apt-get install apache2-utils
Now we can create a secure user for our phpMyAdmin application with the command:
1234
$ sudo htpasswd -c /etc/phpmyadmin/.htpasswd phpmyadminNew password:Re-type new password:Adding password for user phpmyadmin
If for some reason you wanted to give others access to the phpMyAdmin login screen but didn’t want them using your .htaccess credentials, you can create additional secure users with:
1
sudo htpasswd /etc/phpmyadmin/.htpasswd anotheruser
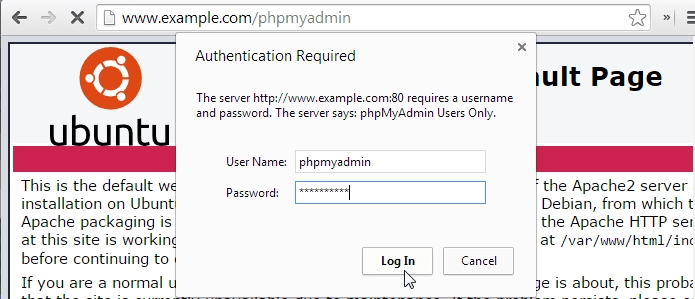
You should now see the .htaccess password prompt we created
While it’s not recommended for production servers, because you have to manually ensure your install of phpMyAdmin is kept up-to-date, you can also install phpMyAdmin from source.
We need to find Apache’s DocumentRoot so we know where to place our phpMyAdmin files:
12
$ grep DocumentRoot /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf DocumentRoot /var/www/html
In this case, we’ll need to put the phpMyAdmin files in /var/www/html.
The stable version of phpMyAdmin at the time this article was written: phpMyAdmin 4.3.11.1 (released 3/4/2015).
Visit the phpMyAdmin download page to grab the latest version of phpMyAdmin.
I ended up with a phpMyAdmin-4.3.11.1-english.tar.gz file in my /var/www/html directory.
123
$ cd /var/www/html$ lsindex.html phpMyAdmin-4.3.11.1-english.tar.gz
1
sudo tar xvzf phpMyAdmin-4.3.11.1-english.tar.gz
Now rename the phpMyAdmin-4.3.11.1-english directory:
1
sudo mv phpMyAdmin-4.3.11.1-english phpmyadmin
Remove the phpMyAdmin files:
1
sudo rm phpMyAdmin-4.3.11.1-english.tar.gz
We want to set up a specific user for our phpMyAdmin install.
12345678910
$ sudo adduser phpmyadminAdding user `phpmyadmin' ...Adding new group `phpmyadmin' (1001) ...Adding new user `phpmyadmin' (1001) with group `phpmyadmin' ...Creating home directory `/home/phpmyadmin' ...Copying files from `/etc/skel' ...Enter new UNIX password:Retype new UNIX password:passwd: password updated successfully
1
sudo chown -R phpmyadmin.phpmyadmin /var/www/html/phpmyadmin
To use the phpMyAdmin install wizard, we first need to set up the config.inc file.
12345
cd /var/www/html/phpmyadminsudo mkdir configsudo chmod o+rw configsudo cp config.sample.inc.php config/config.inc.phpsudo chmod o+w config/config.inc.php
To begin the installation of phpMyAdmin, access the installation URL at:
http://example.com/phpmyadmin/setup/index.php
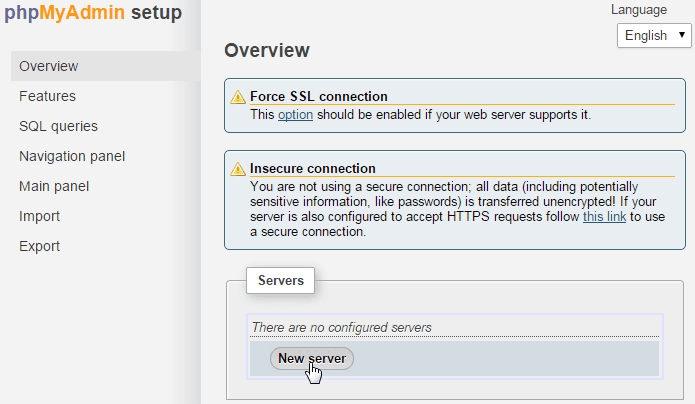
Under the “Servers” section, click on “New Server.”
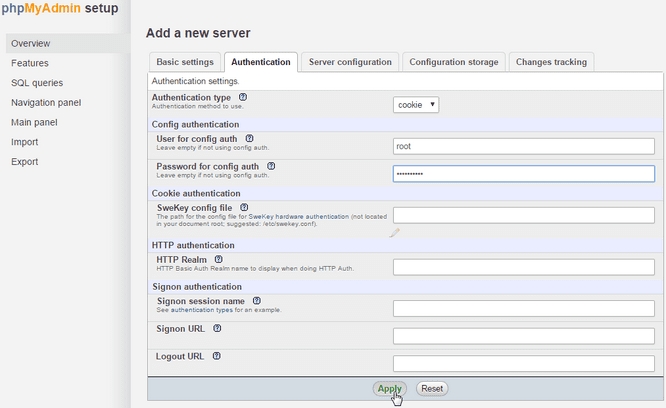
In the “Password for Config Auth” box, type in your MySQL root password.
Remove the phpMyAdmin /config directory for security.
1
sudo rm -rf /var/www/html/phpmyadmin/config
By: Jacob NicholsonUpdated: January 28, 2019Our experts take readers step-by-step through a variety of hosting and programming tasks in our popular series of "How-To" guides. Email
Press TAB to highlight “OK,” then hit ENTER.
Select “Yes” and then hit ENTER at the dbconfig-common screen:
Type it in, hit TAB to highlight “OK,” and then press ENTER.
Next, enter a password for the phpMyAdmin application itself.
Confirm the phpMyAdmin application password.
Log in with the root user and the password you set for the phpMyAdmin application.
Now you’ll see the phpMyAdmin dashboard.
Now if you try to access the phpMyAdmin login, you’ll get the .htaccess password prompt first.
Under the “Servers” section, click on “New Server.”
Under the “Authentication” tab, type in your MySQL root password in the “Password for Config Auth” box and then click “Apply.”